Artists: Tobias Donat, Buck Ellison, Steffen Zillig
Exhibition title: Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures)
Venue: Galerie Conradi, Hamburg, Germany
Date: September 6 – October 26, 2019
Photography: all images copyright and courtesy of the artist and Galerie Conradi, Hamburg
“Being perfect don’t always change shit,” Kanye West, glowing with rage, shouts down from the stage at the end of his concert. He calls on his fans not to be duped by a global elite and the fake news it peddles and instead trust their own feelings. His face is illuminated by the flashlights of the iPhones held up by concertgoers, every one of them an “original,” as Steffen Zillig’s video informs us. Veering between the capitalist commodity aesthetic and truthiness, West is not just trying to (re)enact authenticity: he seeks to shatter the hegemony of a social class that sees itself as both economically and, more importantly, culturally superior. It is an ambition that West, the self-described “greatest artist of all time,” shares with Donald Trump, whom he actively supports—a coalition that seems utterly paradoxical in light of Trump’s racist pronouncements. The re-collectivization of feelings, and especially of the negative feelings of the socially disadvantaged, has conquered the contemporary political terrain. For the right wing, in particular, the emotionalization of public concerns has emerged as a successful strategy allowing it to mobilize people for its exclusionary agendas—at the extreme, for a racist white nationalism. The enemy stereotype limned by its activists includes all those they identify as “others” as well as “cosmopolitans,” who are said to espouse an identity politics of social minorities. The latter label is primarily associated with a social group whose members are portrayed as “academically educated, privileged, and interested in post-materialistic values, the rights of minorities, anti-racism, and the free global movement of humans and capital.”1
The resulting polarization between an overclass and an underclass, Andreas Reckwitz has argued, represents a culturalization of social inequality.2 While the ones aspire to the public display of individuality—his term is singularity—the others rely on an “everyday logic of muddling through”3 and cultivate “plebeian authenticities.”4 These “realizations” of the self are directly interrelated and antithetical, as Pierre Bourdieu already noted in his study of the “taste” of social classes, describing the contradistinction between legitimate and popular taste (with reference to Kant’s distinction between “pure” and “barbarous” taste, which, as a common everyday mindset, privileges amusement over “disinterested pleasure”) as an antagonism between reason and sensuality, between the disavowal and repression of feelings on the one hand and an emphasis on emotions and tendency to embrace the physical on the other. 5
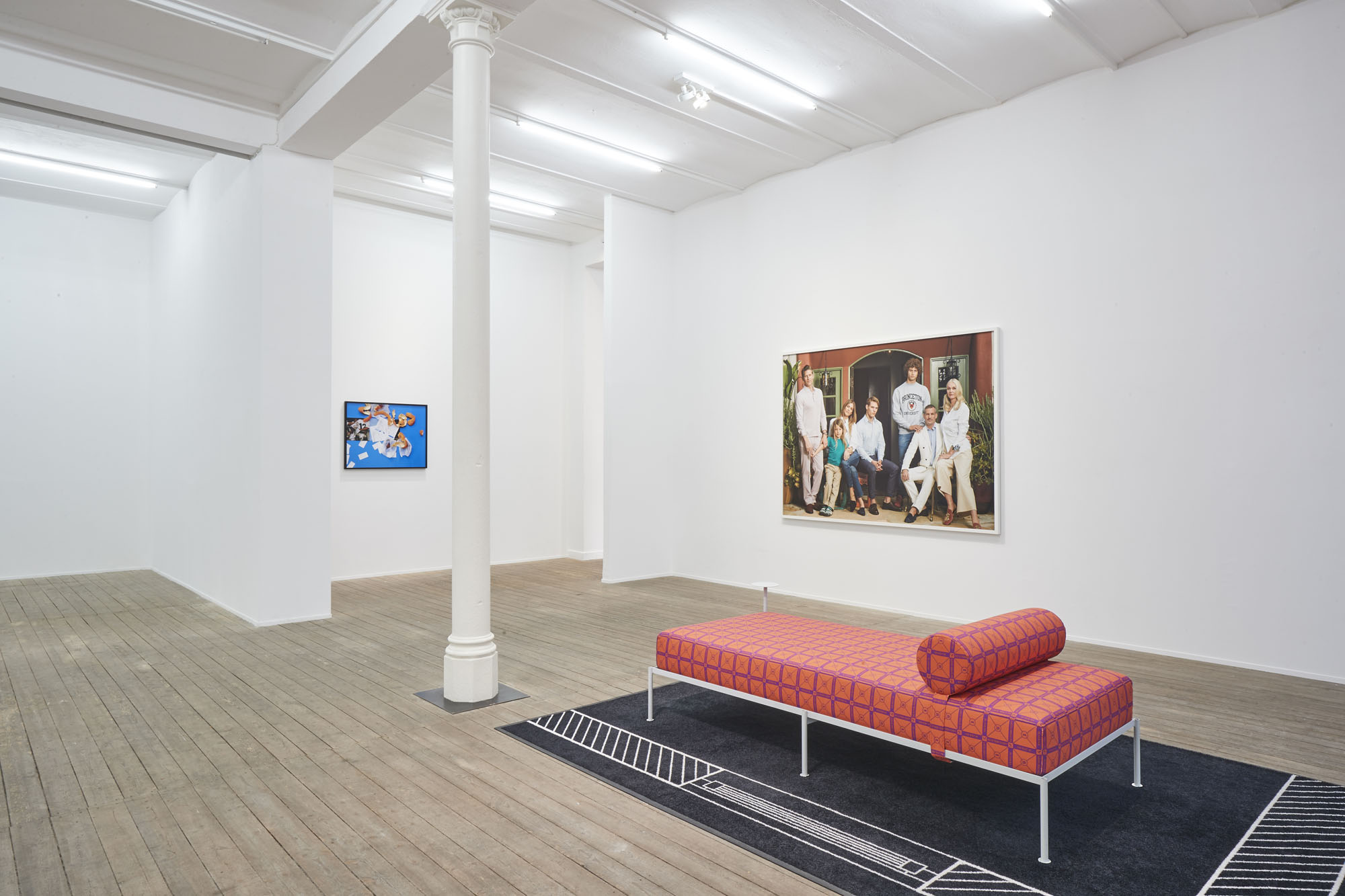
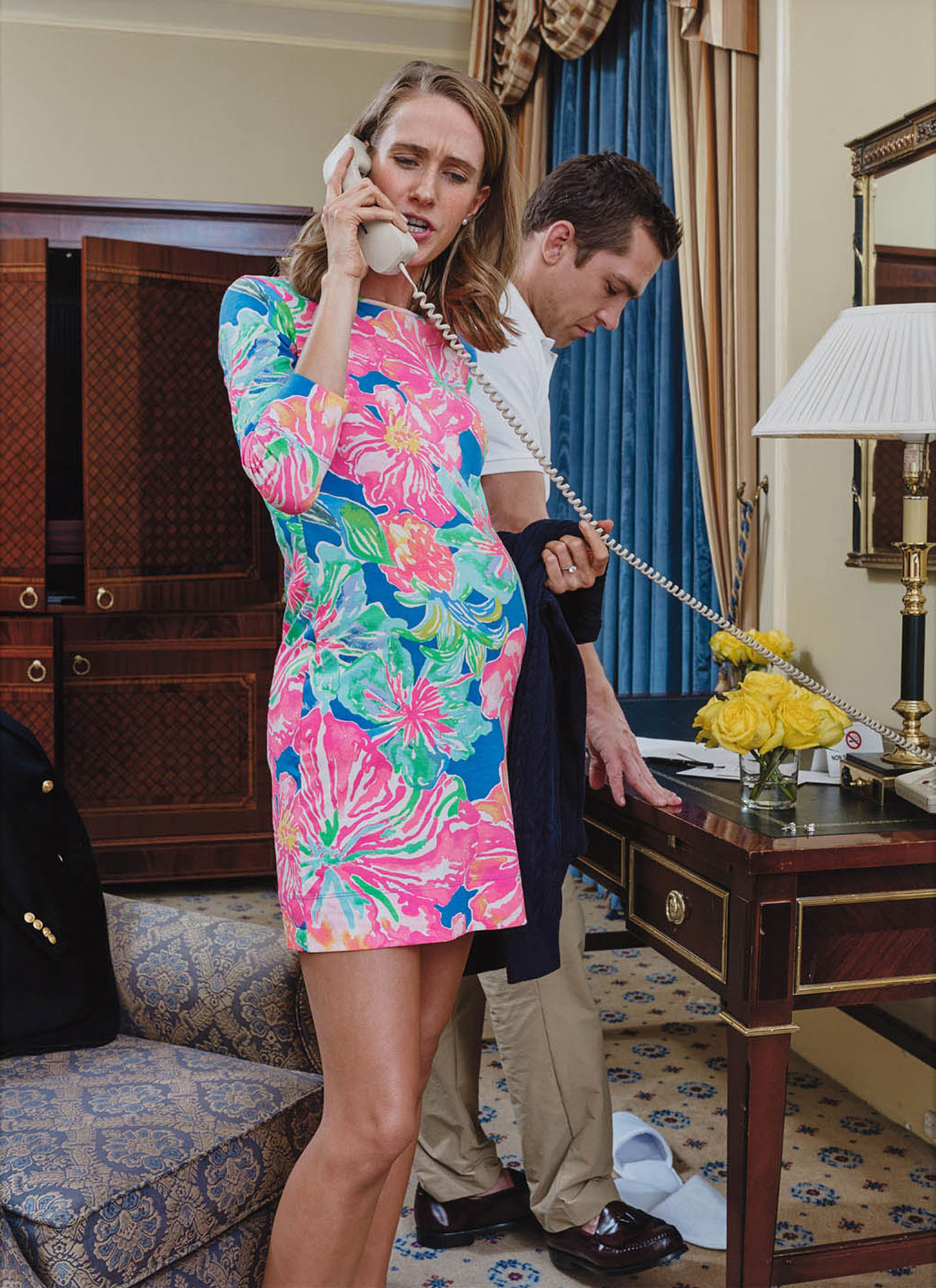
Buck Ellison’s photographs are a prototypical visualization of the impersonal and frosty attitude vis-à-vis the world. His pictures portray the life of the perfect American family—affluent, educated, and white. Each detail functions as a coded signifier of social achievement: tasteful furniture, expensive jewelry, chic clothes, a well-groomed appearance, a toned physique, collectibles from all over the world become the hallmarks of wealth, culture, urbanity, and untiring effort. Emblematic protest, “Pro,” is painted on flawless banners in the teenage offspring’s meticulously tidy room. The only character to register a smidgen of affect—anger—is the pregnant politician in “Dick and Betsy, The Ritz-Carlton, Dallas, Texas.”
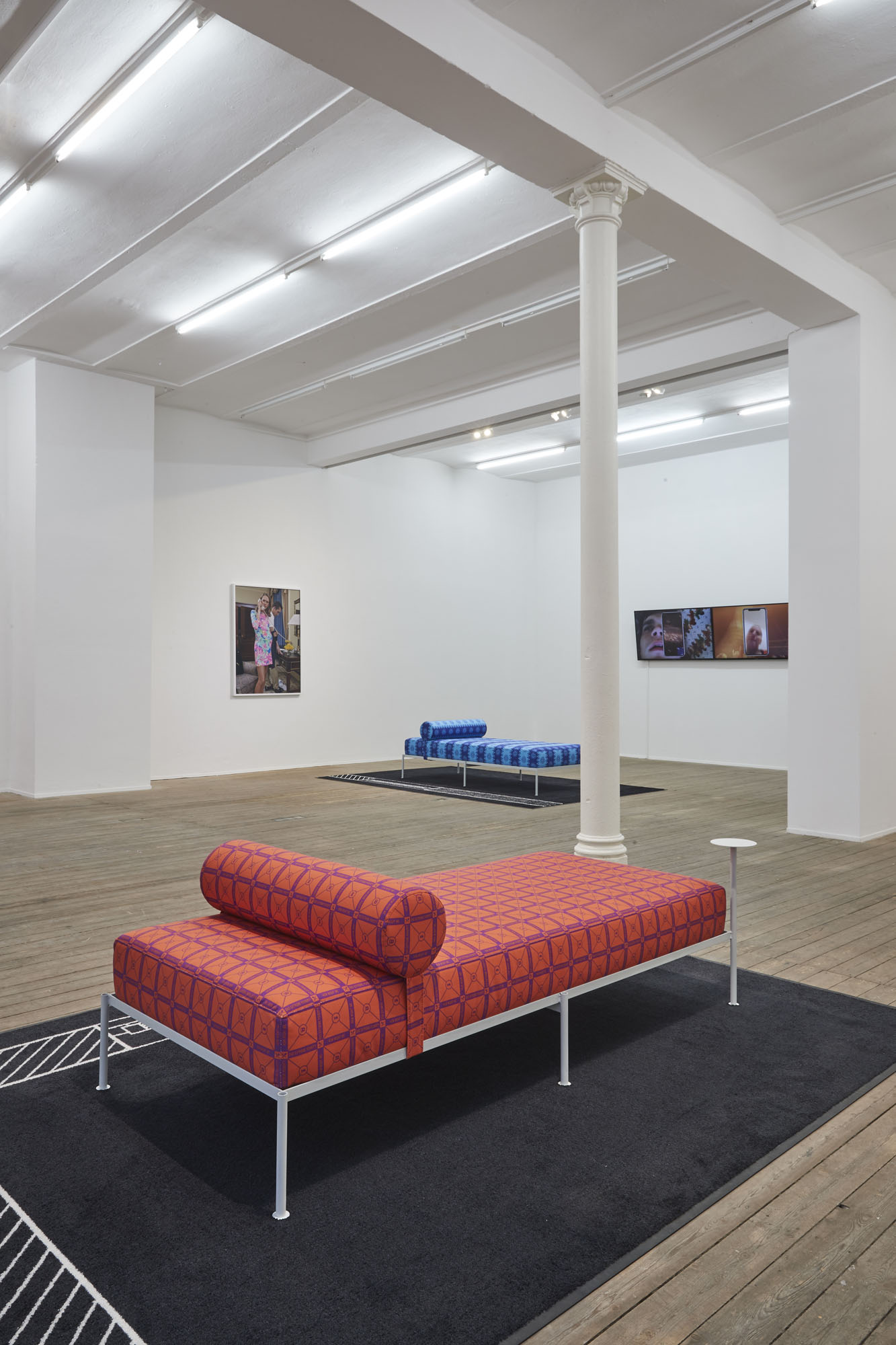
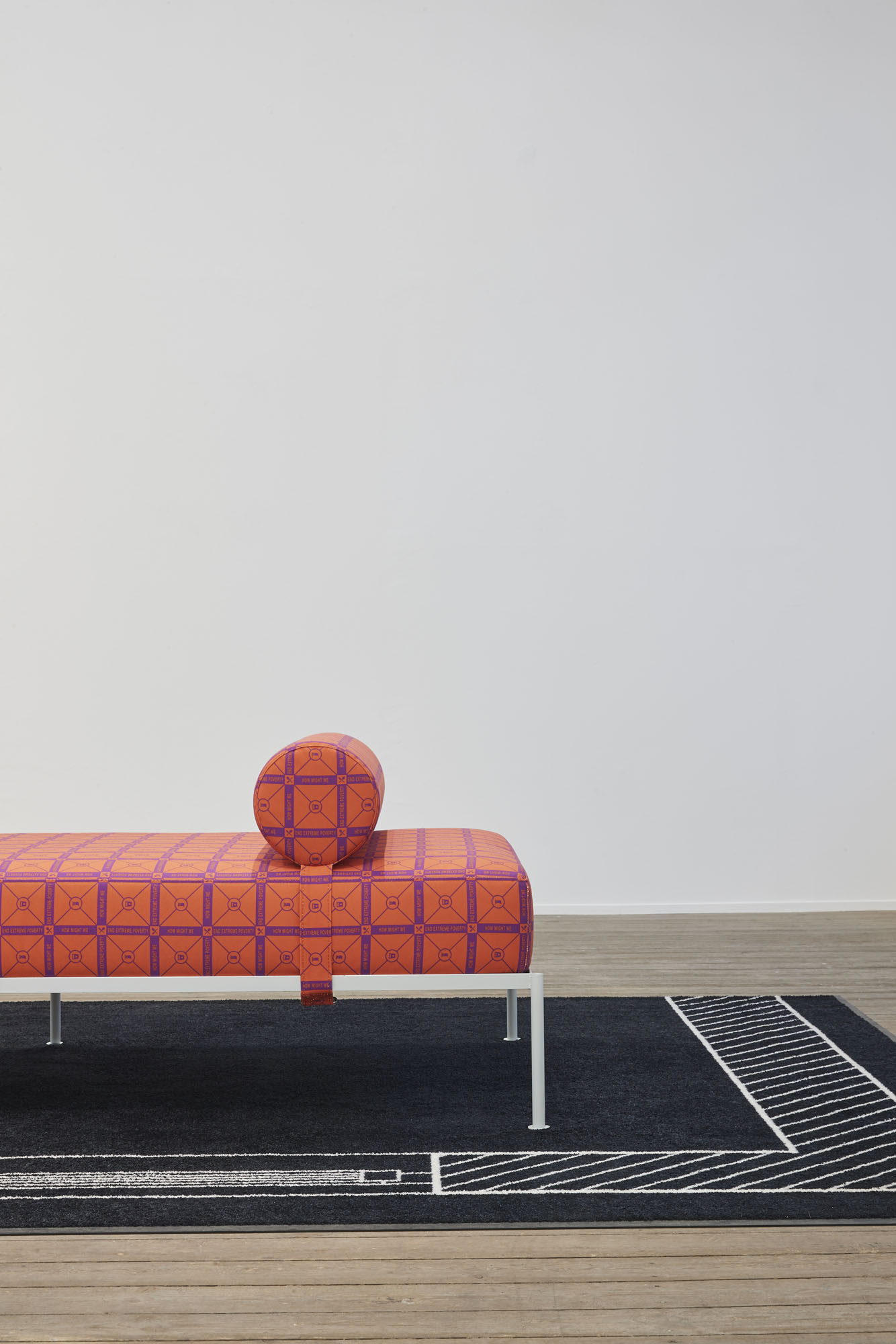
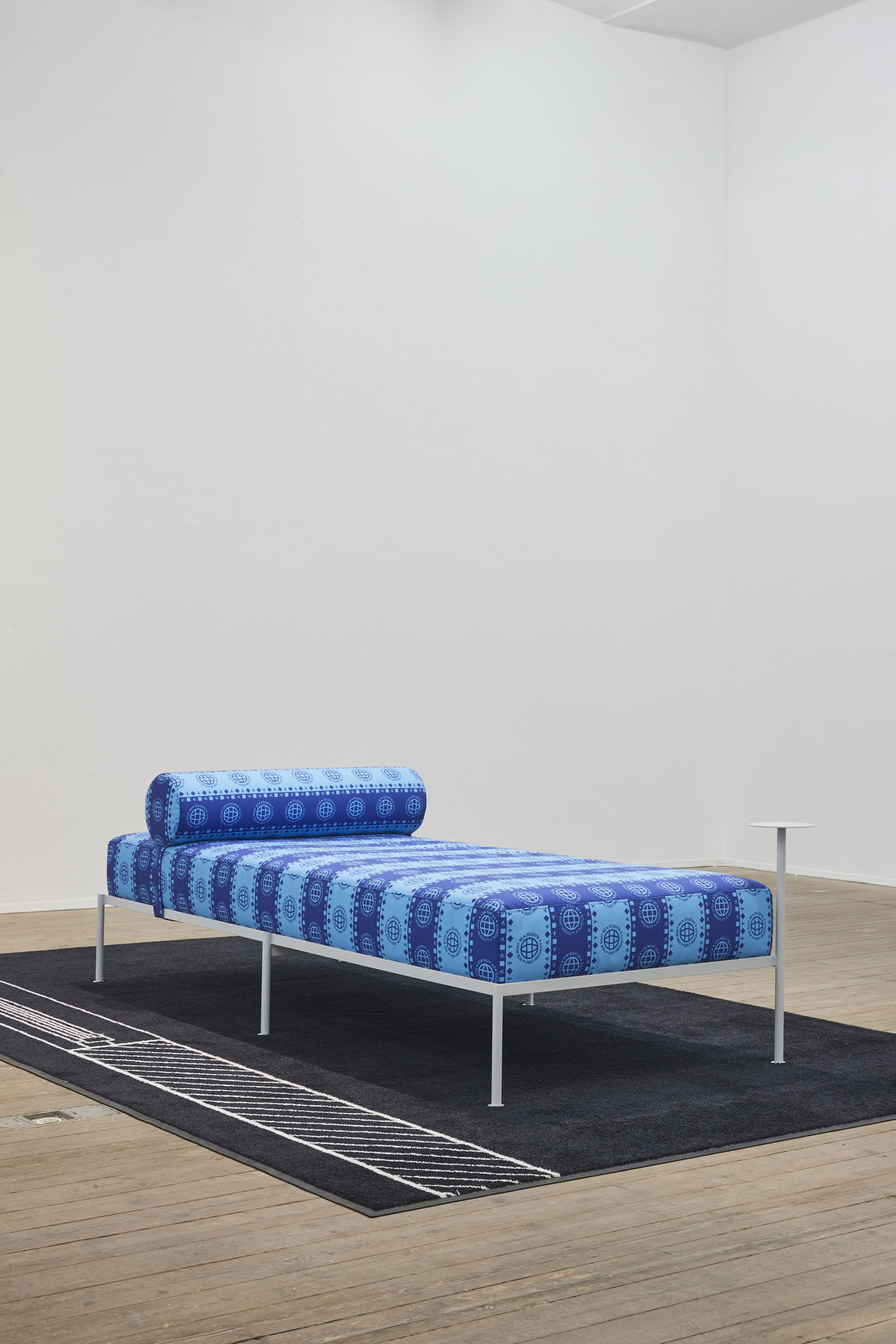
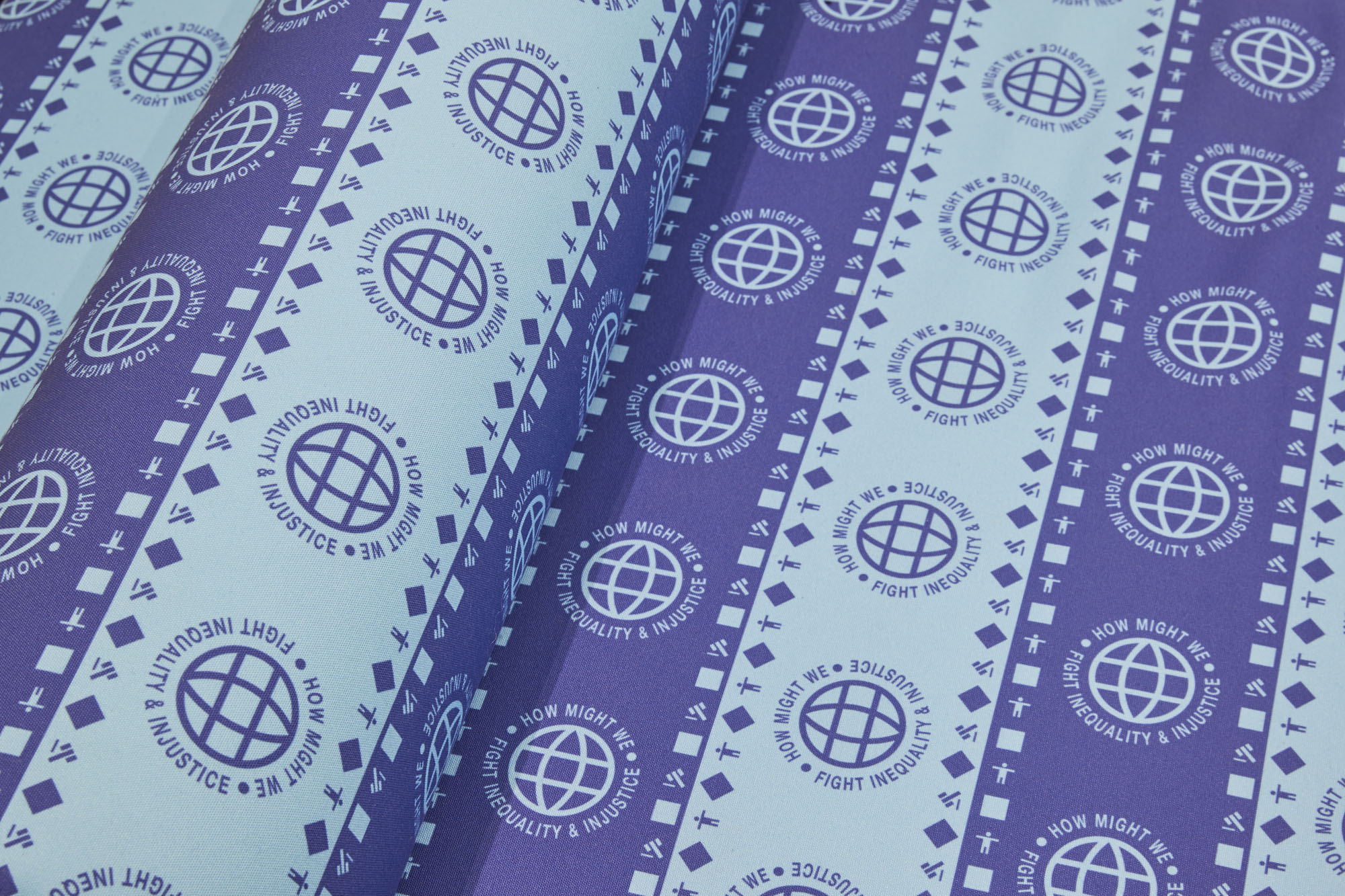
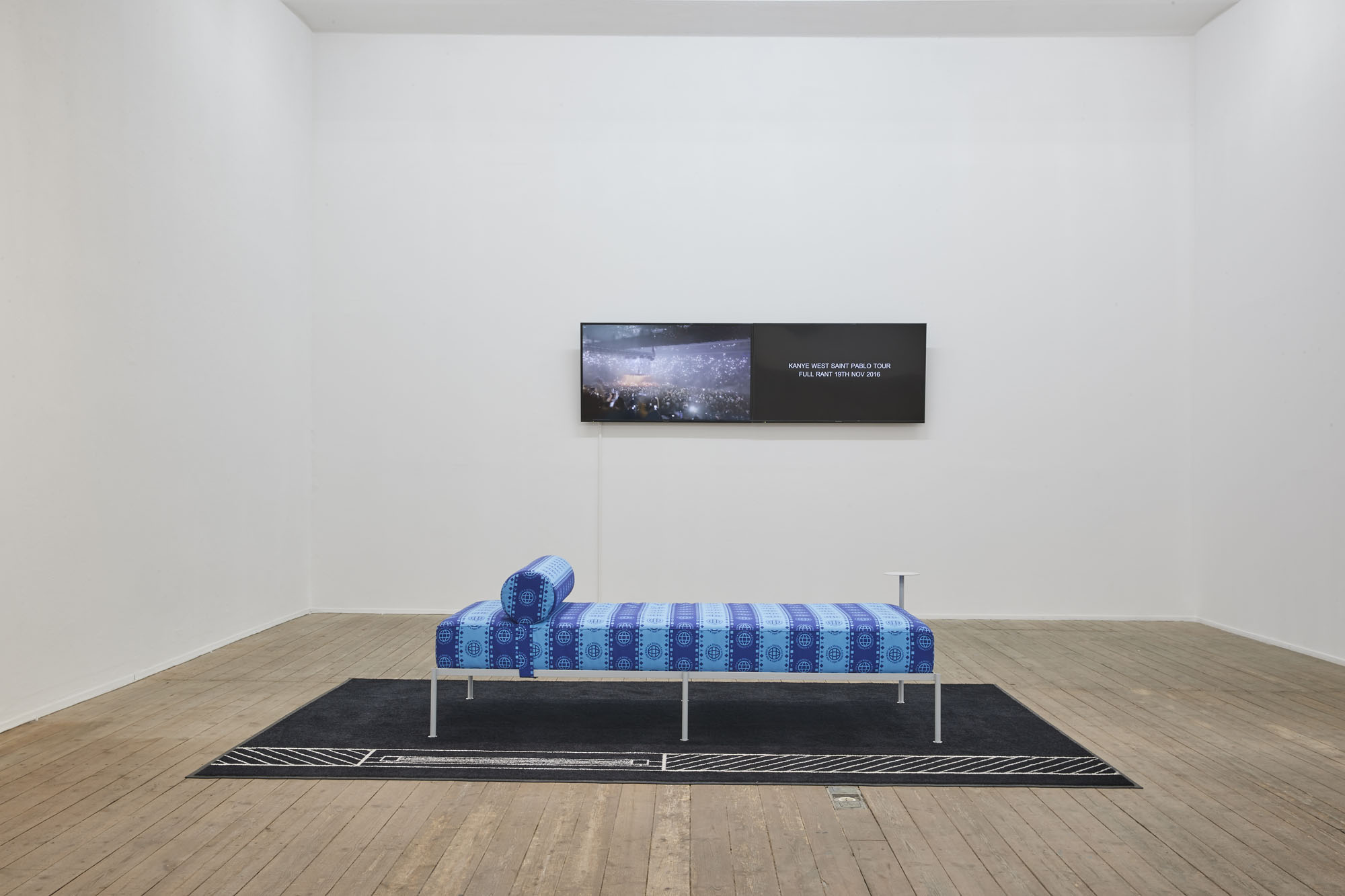
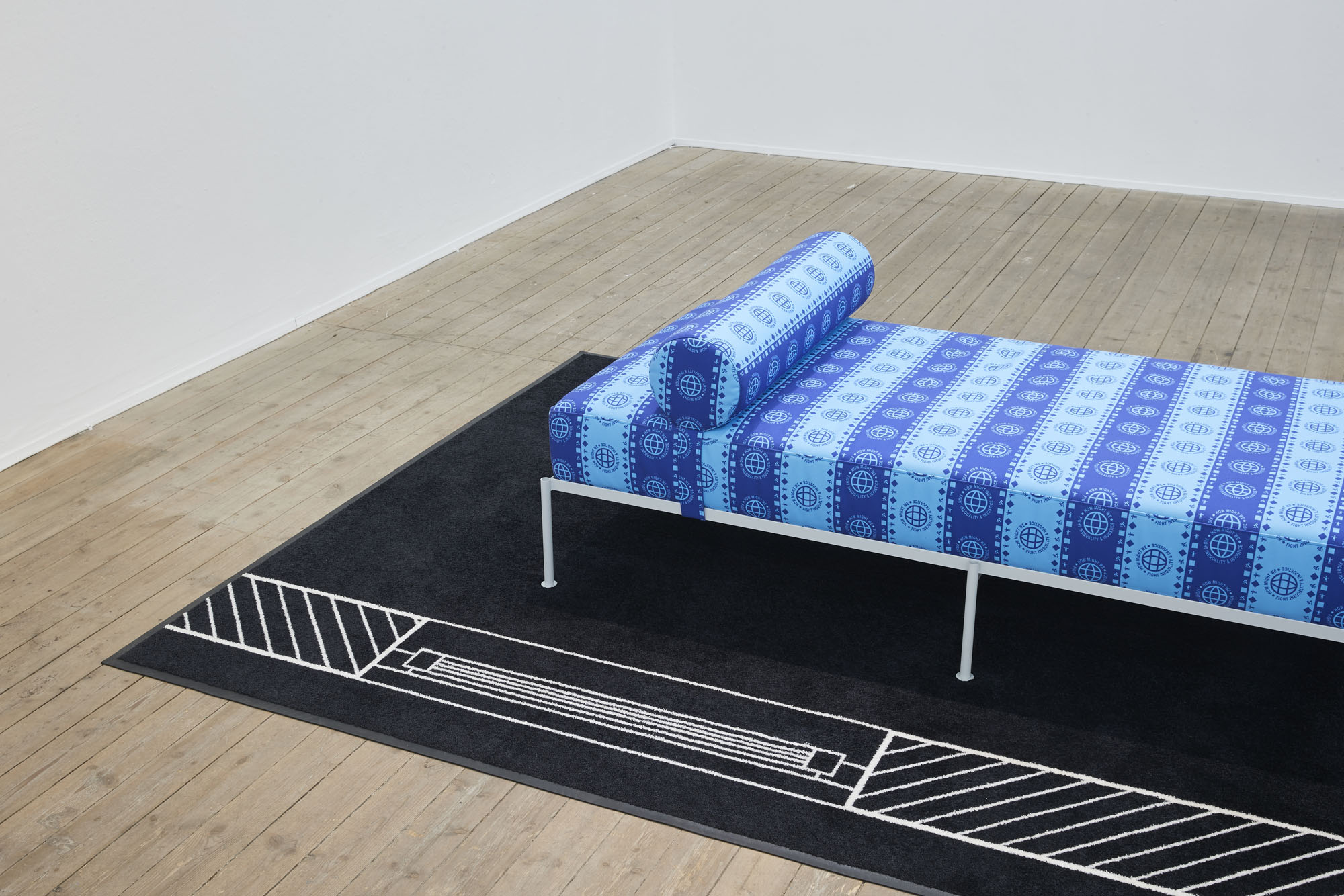
The discrepancy between semblance and activism is also front and center in Tobias Donat’s “Daybeds”: the titles still marshal the Global Sustainable Development Goals adopted by the United Nations in 2015—“How Might We Fight Inequality and Injustice,” “How Might We End Poverty”—but the formal reference becomes utterly vacuous when repeated ad infinitum as a pattern on fabric covers. The daybed itself, presented by Donat in a contemporary, aesthetic-minimalist version, similarly reads as an attribute of a social milieu whose lived reality is characterized by independence and self-organization. Unlike the regulated employment relationship, project-based and putatively free labor gives the worker flexibility to structure his or her day, spent in the stylishly furnished home office.
As Luc Boltanski and Ève Chiapello have shown6, the seemingly emancipatory quest for greater self-determination and autonomy has been coopted by a flexible capitalism and turned against itself. Even worse, self-expression and uniqueness have become obligatory for all members of society, a doctrinaire vision that has gone hand in hand with the devaluation of other ideas on how to live: the cultural self-empowerment of the new middle class requires the denigration of the lifestyles of the lower classes. And the maxim of perfection through self-discipline meets its antipode in the yearning for disinhibition and escalation.
Processes of singularization within the neoliberal logic as described by Reckwitz have created a situation in which feelings of being devalued and defeated appear not so much as class positions but rather as lamentable individual cases. Yet when these diffuse sentiments are deftly addressed and re-collectivized, they generate a distinctive political momentum, as Cornelia Koppetsch points out. Holding others responsible for a subjectively perceived decline in social status breeds resentment. It is not social inequality as such but the collective activation of its felt reality, she argues, that prompts political action.7 Resentments are in play in both political camps, serving to devalue those above as well as those below. In a globalized world, media are also instrumental to the genesis of communities of feeling and the growing tribalization of society.8 And finally, “polarization and cultural division […] are a big business as well.
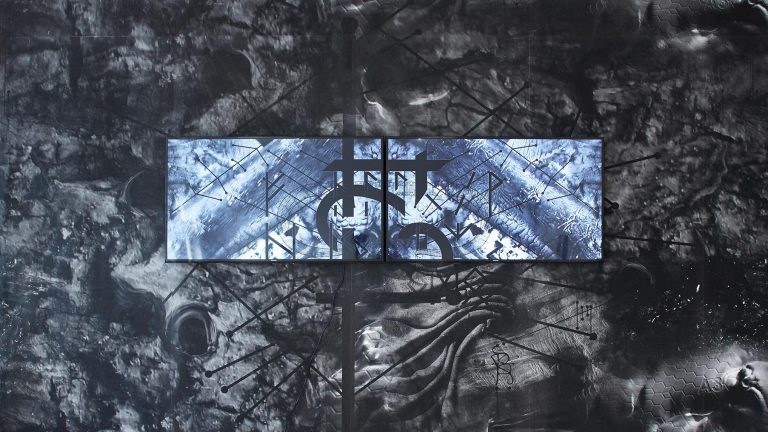
Many media have an interest in fanning their consumers’ feelings of being disrespected or confirming their victimhood as members of a silenced and disenfranchised majority.”9 The contemporary imperative of self-realization defines success not just as (economic and social) security but primarily as the permanent reinvention of an interesting and authentic life. The fear of failure unleashes the self-satisfied denigration of “others” and is vented in emotional outbursts. Zillig’s “Only Originals” shines a spotlight on what happens when the appeal to these emotions is paired with narcissism and ignorance; or, worse, confounds the poles of class and nation. The individual’s pursuit of recognition as an end in itself fans the eruptions and escalations of those who long for deliverance from the constant pressure to perform.
The American journalist and writer Ta-Nehisi Coates has pinpointed these ambivalences in a critical essay: “West calls his struggle the right to be a ‘free thinker,’ and he is, indeed, championing a kind of freedom—a white freedom, freedom without consequence, freedom without criticism, freedom to be proud and ignorant; freedom to profit off a people in one moment and abandon them in the next; a Stand Your Ground freedom, freedom without responsibility, without hard memory […].”10
–Juliane Bischoff
(1) Silke van Dyk, “Identitätspolitik gegen ihre Kritik gelesen: Für einen rebellischen Universalismus,” in Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung (ed.): Aus Politik und Zeitgeschichte 9–11/2019, “Identitätspolitik,” 26.
(2) See Andreas Reckwitz, Die Gesellschaft der Singularitäten: Zum Strukturwandel der Moderne, 5th ed. (Berlin: Suhrkamp, 2018), 350.
(3) Ibid., 351.
(4) Ibid., 361.
(5) See Pierre Bourdieu, Distinction: A Social Critique of the Judgment of Taste, trans. Richard Nice (Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press, 1984), 492–94.
(6) See Luc Boltanski and Ève Chiapello, The New Spirit of Capitalism, trans. Gregory Elliott (London and New York: Verso, 2005).
(7) See Cornelia Koppetsch, “Ressentiments: Über die politische Wirkmächtigkeit negativer Gefühle,” December 20, 2018, soziopolis.de/beobachten/gesellschaft/artikel/ressentiments/ (accessed August 12, 2019).
(8) See ibid.
(9) Jan-Werner Müller, “‘Das wahre Volk’ gegen alle anderen: Rechtpopulismus als Identitätspolitik,” in Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung (ed.): Aus Politik und Zeitgeschichte 9–11/2019, “Identitätspolitik,” 23.
(10) Ta-Nehisi Coates, “I’m Not Black, I’m Kanye: Kanye West Wants Freedom—White Freedom,” May 7, 2018, theatlantic.com/entertainment/archive/2018/05/im-not-black-im-kanye/559763/ (accessed August 12, 2019).
Buck Ellison, Untitled (Christmas Card), 2018, Archival pigment print, 116.7 × 160 cm, Courtesy of the artist, The Sunday Painter (London) and Balice Hertling (Paris)
Front: Tobias Donat, Back: Buck Ellison, Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures), 2019, Exhibition view, Conradi
Tobias Donat, How Might We End Extreme Poverty, 2018, Daybed 01 by Buero Kofink Schels, digital print on canvas and digital print on hightwist nylon, 200 x 300 cm, Courtesy of the artist and Buero Kofink Schels
Tobias Donat, How Might We End Extreme Poverty (Detail), 2018, Courtesy of the artist and Buero Kofink Schels
Front: Tobias Donat, Back: Buck Ellison, Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures), 2019 Exhibition view, Conradi
Buck Ellison, Husbands, 2014, Archival inkjet print, 56 x 71 cm, Courtesy of the artist, The Sunday Painter (London) and Balice Hertling (Paris)
Buck Ellison, Husbands, 2014, Archival inkjet print, 56 x 71 cm, Courtesy of the artist, The Sunday Painter (London) and Balice Hertling (Paris)
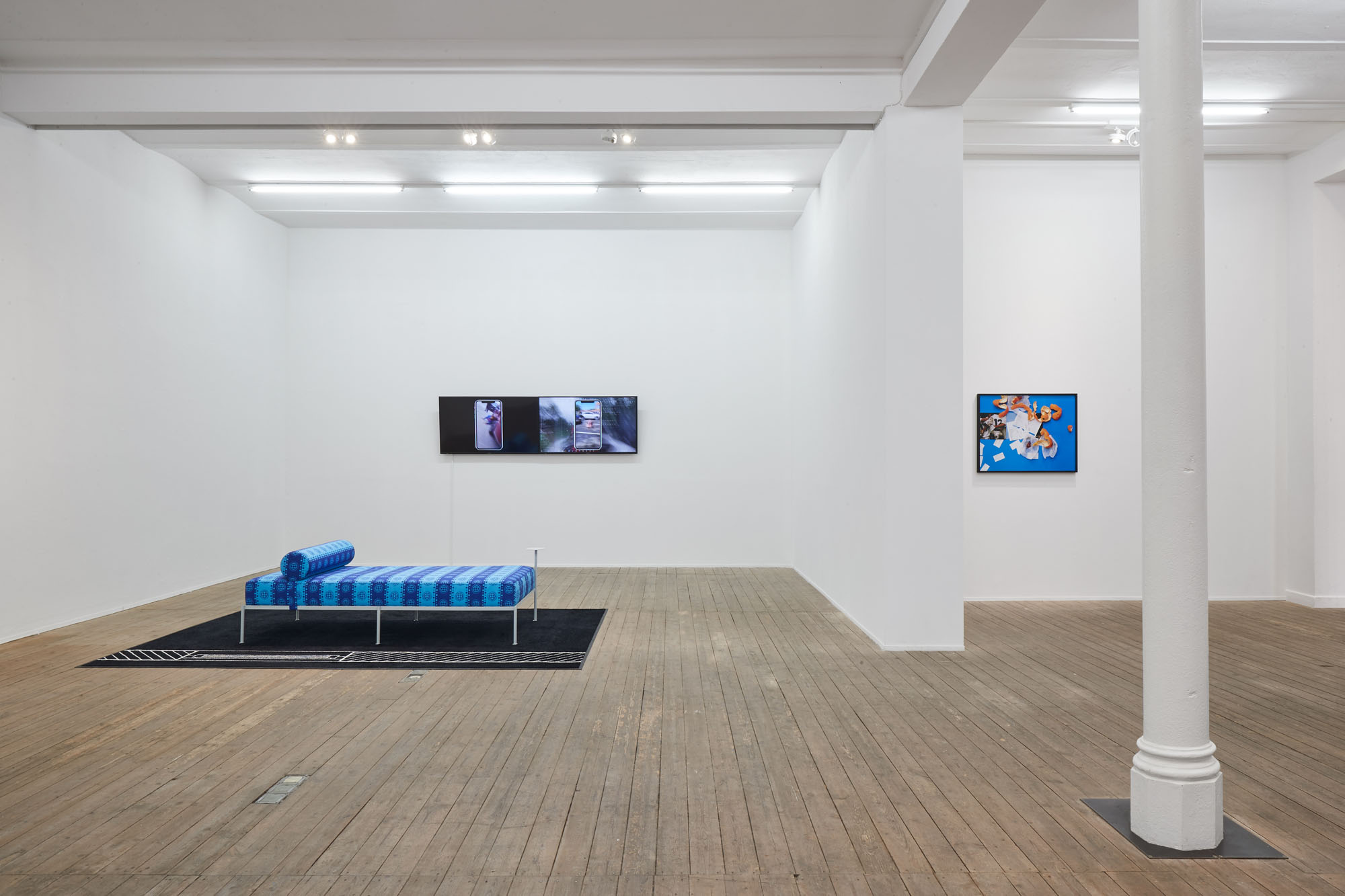
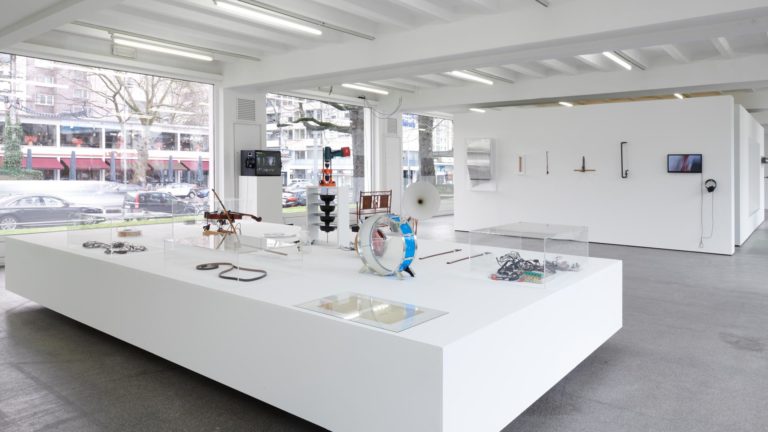
Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures), 2019, Exhibition view, Conradi
Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures), 2019, Exhibition view, Conradi
Tobias Donat, How Might We Fight Inequality and Injustice, 2018, Daybed 01 by Buero Kofink Schels, digital print on canvas and digital print on hightwist nylon, 200 x 300 cm, Courtesy of the artist and Buero Kofink Schels
Tobias Donat, How Might We Fight Inequality and Injustice (Detail), 2018, Courtesy of the artist and Buero Kofink Schels
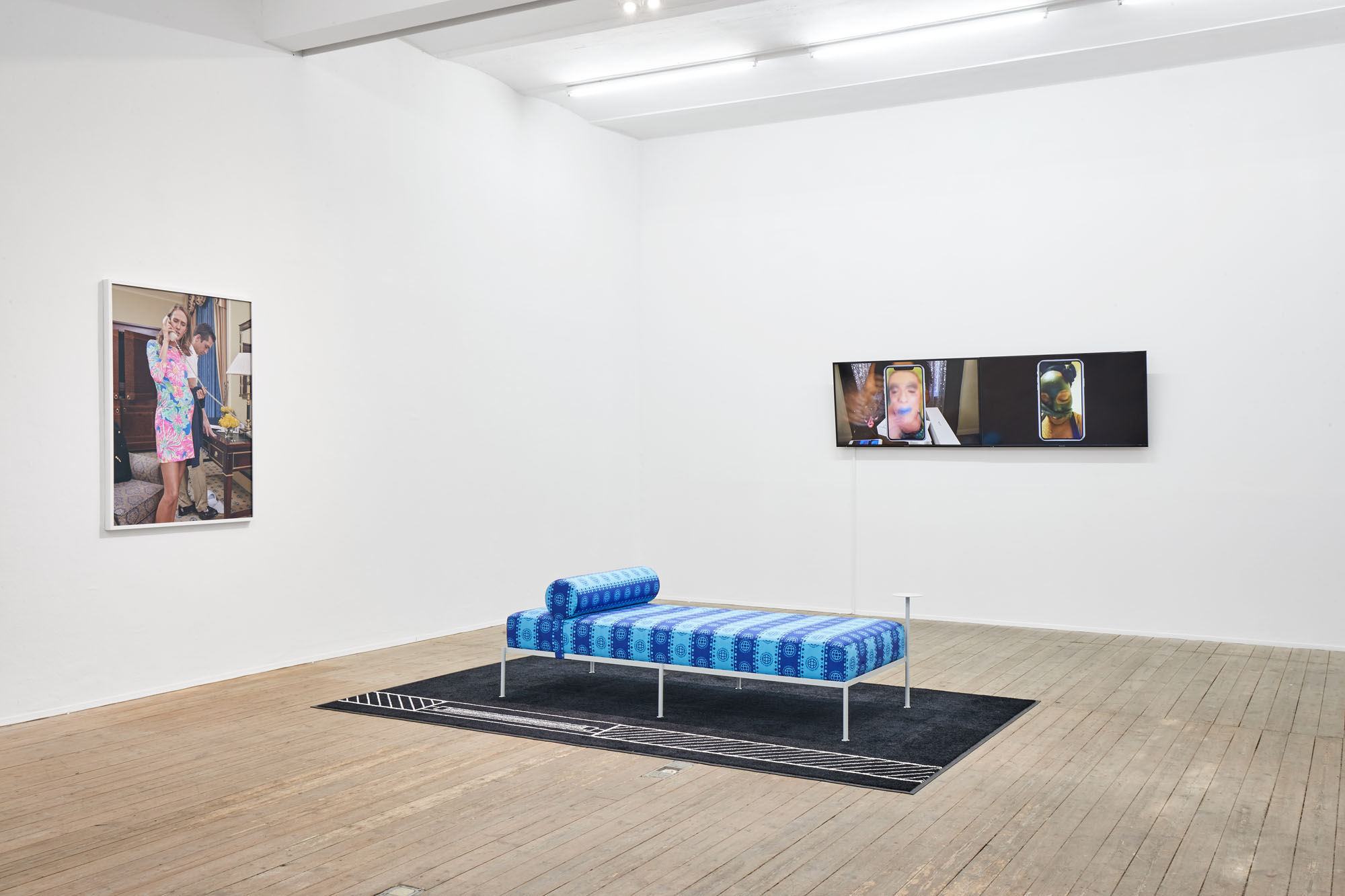
Left: Buck Ellison, Center: Tobias Donat, Right: Steffen Zillig, Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures), 2019, Exhibition view, Conradi
Buck Ellison, Dick and Betsy, The Ritz-Carlton, Dallas, Texas, 2019, Archival pigment print, 102 x 87 cm, Courtesy of the artist, The Sunday Painter (London) and Balice Hertling (Paris)
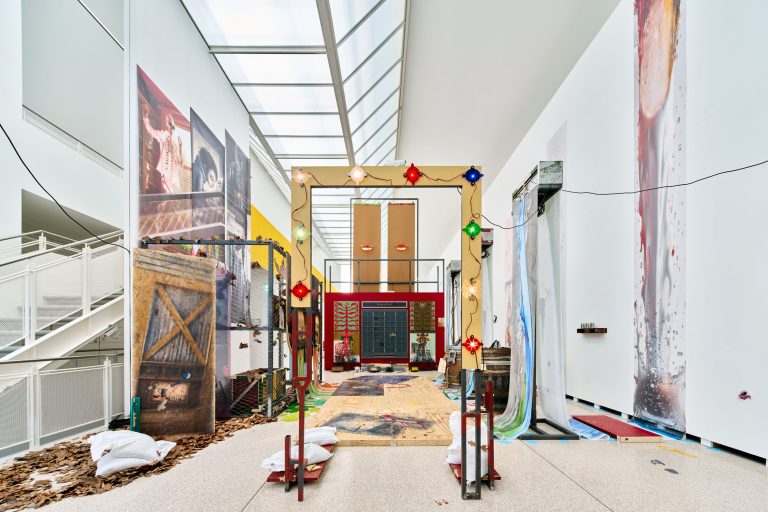
Front: Tobias Donat, Back: Steffen Zillig, Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures), 2019, Exhibition view, Conradi
Steffen Zillig, Only Originals, 2018, two-channel HD video collage, color, sound, 19‘, Exhibition view, Conradi
Steffen Zillig, Only Originals, 2018, video still, two-channel HD video collage, color, sound, 19‘, Courtesy of the artist and Conradi (Hamburg)
Tobias Donat, How Might We Fight Inequality and Injustice, 2018, Daybed 01 by Buero Kofink Schels, digital print on canvas and digital print on hightwist nylon, 200 x 300 cm, Courtesy of the artist and Buero Kofink Schels
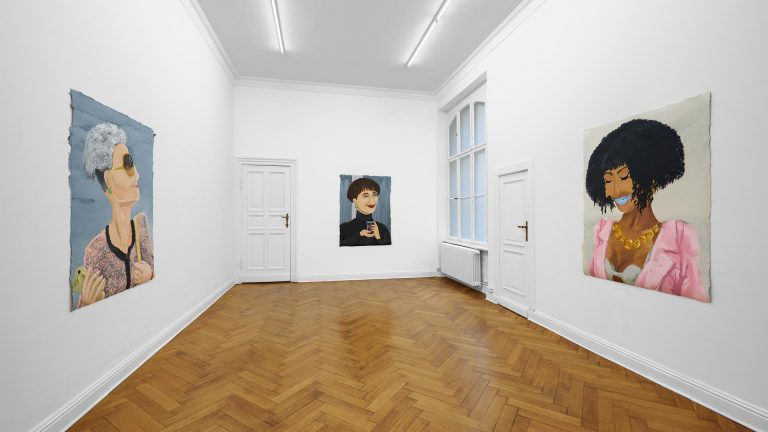
Left: Tobias Donat, Right: Buck Ellison , Sittenbilder (Genre Pictures), 2019, Exhibition view, Conradi
Buck Ellison, Pro, 2016, Archival pigment print, 116 x 146 cm, Courtesy of the artist, The Sunday Painter (London) and Balice Hertling (Paris)
Buck Ellison, Pro, 2016, Archival pigment print, 116 x 146 cm, Courtesy of the artist, The Sunday Painter (London) and Balice Hertling (Paris)